Which of the following statements about sepsis is false? Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the body’s response to an infection damages its own tissues and organs. It is a medical emergency that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment.
This article will explore the various aspects of sepsis, including its definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, management, and prevention.
Definition of Sepsis: Which Of The Following Statements About Sepsis Is False
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition characterized by a systemic inflammatory response to infection. It is a complex and potentially fatal condition that can lead to organ dysfunction, tissue damage, and even death.
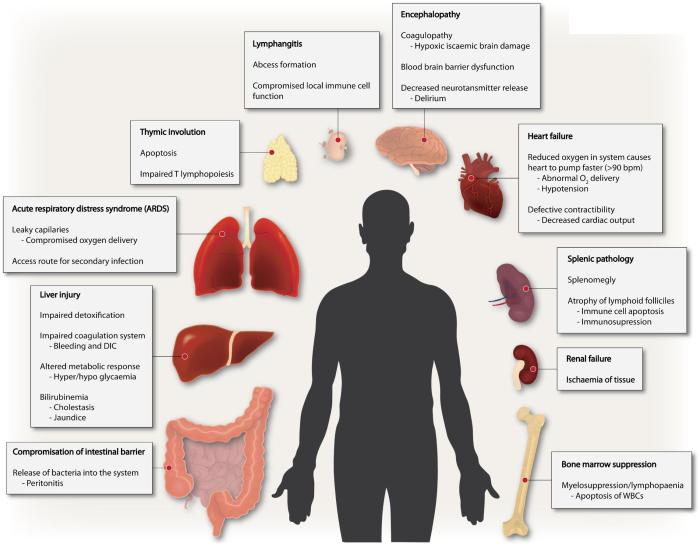
The pathophysiology of sepsis involves a cascade of inflammatory reactions triggered by the presence of pathogens or their components in the bloodstream. This inflammatory response leads to widespread activation of immune cells, release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and increased vascular permeability.
Clinical Manifestations of Sepsis
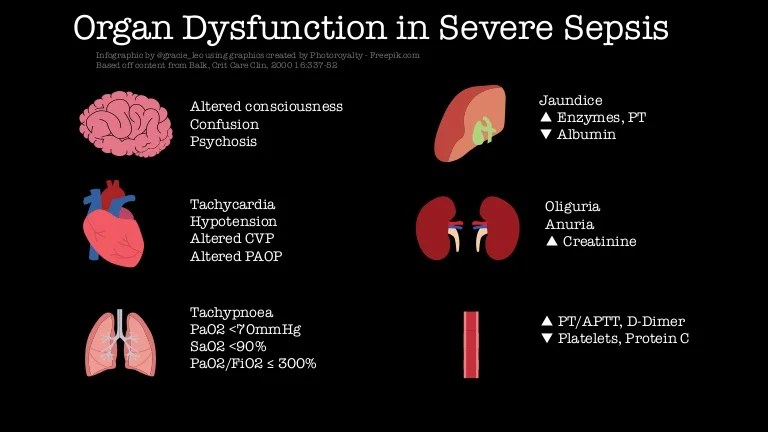
Sepsis is often associated with a constellation of clinical signs and symptoms known as systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). SIRS criteria include:
- Temperature >38.3°C or<36°C
- Heart rate >90 beats per minute
- Respiratory rate >20 breaths per minute or PaCO2<32 mmHg
- White blood cell count >12,000/mm3 or<4,000/mm3
In addition to SIRS, sepsis may also present with organ dysfunction, such as hypotension, oliguria, or altered mental status.
Sepsis screening tools, such as the qSOFA or SOFA score, can be used to help identify patients at risk for sepsis and facilitate early intervention.
Causes and Risk Factors of Sepsis
The most common causes of sepsis are infections, including:
- Pneumonia
- Urinary tract infections
- Intra-abdominal infections
- Skin and soft tissue infections
Non-infectious triggers, such as trauma, burns, or pancreatitis, can also lead to sepsis.
Risk factors for sepsis include:
- Age (very young or elderly)
- Underlying medical conditions (diabetes, immunosuppression, etc.)
- Recent surgery or invasive procedures
Management of Sepsis, Which of the following statements about sepsis is false
Early recognition and management of sepsis are crucial to improve patient outcomes. The key principles of sepsis management include:
- Early administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics
- Fluid resuscitation to maintain adequate tissue perfusion
- Vasopressor support to maintain blood pressure
- Inotropic support to improve cardiac function
- Source control, such as surgical drainage of an infected abscess
Complications and Prognosis of Sepsis
Sepsis can lead to a range of complications, including:
- Organ failure
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
- Septic shock
The prognosis of sepsis depends on the severity of infection, host factors, and timely treatment. Mortality rates for severe sepsis can be as high as 50%.
Sepsis survivors may experience long-term consequences, such as:
- Cognitive impairment
- Physical disabilities
- Increased risk of future infections
Prevention of Sepsis
Infection prevention and control measures are essential to reduce the risk of sepsis. These measures include:
- Vaccination
- Hand hygiene
- Antimicrobial stewardship
Early detection and management of infections can also help prevent the development of sepsis.
FAQ
What is the most common cause of sepsis?
The most common cause of sepsis is infection, particularly pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and abdominal infections.
What are the early signs and symptoms of sepsis?
Early signs and symptoms of sepsis include fever, chills, rapid heart rate, rapid breathing, and confusion.
How is sepsis diagnosed?
Sepsis is diagnosed based on clinical criteria, such as the presence of infection and systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS).
What is the treatment for sepsis?
Treatment for sepsis includes antibiotics to treat the infection, intravenous fluids to restore blood pressure, and vasopressors to support blood flow.
What are the complications of sepsis?
Complications of sepsis include organ failure, septic shock, and death.