Which microscopic field contains a hypertonic solution? This intriguing question delves into the fascinating realm of microscopy, where hypertonic solutions play a pivotal role in shaping microscopic structures and advancing research endeavors. From understanding their characteristics to unraveling their effects on microscopic components, this exploration unveils the significance of hypertonic solutions in the microscopic domain.
Hypertonic solutions, characterized by their higher solute concentration compared to the surrounding environment, exert a remarkable influence on microscopic structures. They possess the ability to alter the shape, size, and function of these structures, making them invaluable tools for researchers seeking to manipulate and study microscopic systems.
Definition of Hypertonic Solution
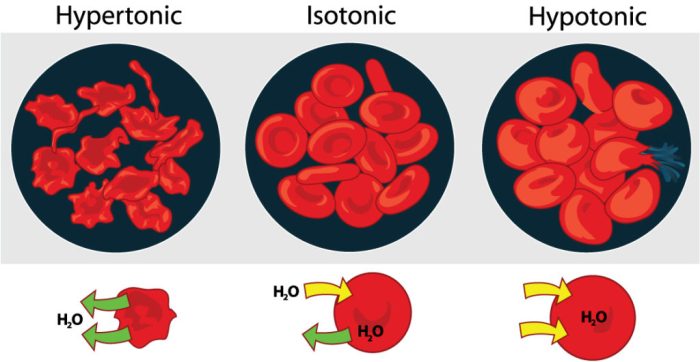
A hypertonic solution is a solution with a higher solute concentration than the solution it is compared to. In simpler terms, it contains a higher concentration of dissolved particles compared to another solution. The solute concentration is the amount of dissolved substance present in a given volume of solvent.
Characteristics and Properties of Hypertonic Solutions, Which microscopic field contains a hypertonic solution
- Higher solute concentration:Hypertonic solutions have a greater concentration of dissolved particles than the solution they are compared to.
- Osmotic pressure:Hypertonic solutions exert a higher osmotic pressure than the solution they are compared to. Osmotic pressure is the pressure that drives water molecules from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
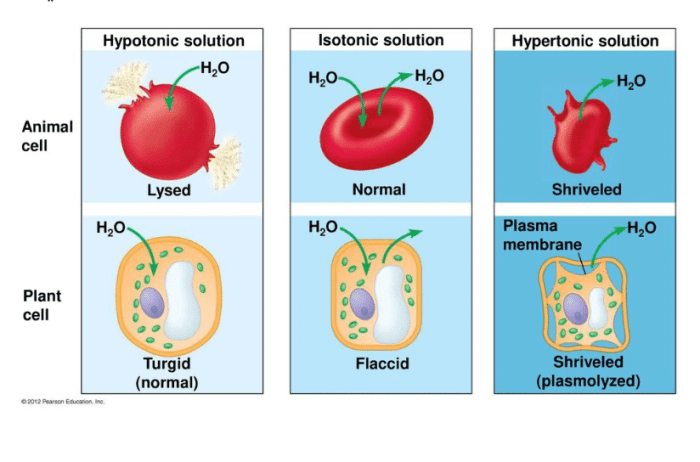
- Cell shrinkage:When cells are placed in a hypertonic solution, water molecules move out of the cells in an attempt to equalize the solute concentration on both sides of the cell membrane. This causes the cells to shrink.
Microscopic Field Containing Hypertonic Solution

Hypertonic solutions are commonly found in the microscopic field of cell biology. They are used to study the effects of osmotic pressure on cells.
In cell biology, hypertonic solutions are used to:
- Study cell volume regulation:Hypertonic solutions can be used to study how cells regulate their volume in response to changes in osmotic pressure.
- Investigate cell membrane permeability:Hypertonic solutions can be used to investigate the permeability of cell membranes to water and other solutes.
- Induce cell death:Hypertonic solutions can be used to induce cell death by causing cells to shrink and lose their function.
Examples of Hypertonic Solutions in Microscopic Fields
- Sucrose solution:A sucrose solution is a commonly used hypertonic solution in cell biology. It is often used to study the effects of osmotic pressure on cells.
- NaCl solution:A NaCl solution is another commonly used hypertonic solution in cell biology. It is often used to investigate the permeability of cell membranes to water and other solutes.
- Mannitol solution:A mannitol solution is a hypertonic solution that is often used to induce cell death. It is used in some medical procedures, such as the treatment of brain edema.
Effects of Hypertonic Solutions on Microscopic Structures
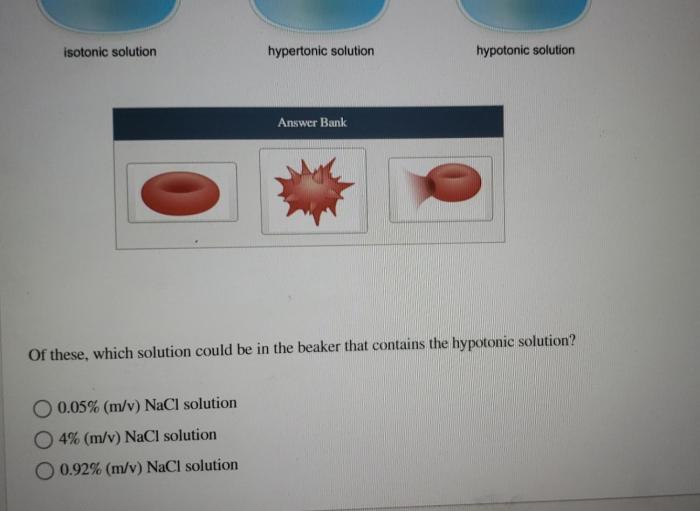
Hypertonic solutions can have a variety of effects on microscopic structures, including:
- Cell shrinkage:As mentioned earlier, hypertonic solutions can cause cells to shrink. This is due to the movement of water molecules out of the cells in an attempt to equalize the solute concentration on both sides of the cell membrane.
- Changes in cell shape:Hypertonic solutions can also cause changes in cell shape. For example, red blood cells placed in a hypertonic solution will become crenated, or scalloped.
- Inhibition of cell division:Hypertonic solutions can inhibit cell division by preventing the cells from taking up enough water to grow and divide.
Methods for Creating Hypertonic Solutions
Hypertonic solutions can be created by dissolving a solute in a solvent. The concentration of the hypertonic solution will depend on the amount of solute that is dissolved.
It is important to note that the concentration of the hypertonic solution must be carefully controlled. If the solution is too concentrated, it can damage or kill cells. If the solution is not concentrated enough, it will not have the desired effect.
Applications of Hypertonic Solutions in Microscopic Research
Hypertonic solutions have a variety of applications in microscopic research, including:
- Studying cell volume regulation:Hypertonic solutions can be used to study how cells regulate their volume in response to changes in osmotic pressure. This information can be used to develop new treatments for conditions such as cell dehydration and edema.
- Investigating cell membrane permeability:Hypertonic solutions can be used to investigate the permeability of cell membranes to water and other solutes. This information can be used to develop new drugs and treatments for conditions such as cancer and diabetes.
- Inducing cell death:Hypertonic solutions can be used to induce cell death by causing cells to shrink and lose their function. This information can be used to develop new treatments for conditions such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
FAQ Compilation: Which Microscopic Field Contains A Hypertonic Solution
What is a hypertonic solution?
A hypertonic solution is a solution that has a higher solute concentration than the surrounding environment.
What are the effects of hypertonic solutions on microscopic structures?
Hypertonic solutions can alter the shape, size, and function of microscopic structures.
How are hypertonic solutions used in microscopic research?
Hypertonic solutions are used in microscopic research to manipulate and study microscopic structures.