The process for reproducing shading in print is a complex and multifaceted one, involving a range of techniques, challenges, and applications. From halftoning to stochastic screening, the methods used to create the illusion of shading vary widely, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Understanding the factors that affect the quality of shading reproduction, such as screen ruling, dot shape, and ink density, is essential for achieving optimal results.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of reproducing shading in print, providing a detailed overview of the steps involved, from image preparation to printing. It also explores the common challenges encountered, such as moiré patterns, banding, and color shifts, and offers strategies for overcoming them.
By examining print samples that illustrate these challenges and solutions, readers gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of this process.
Techniques for Reproducing Shading in Print: Process For Reproducing Shading In Print
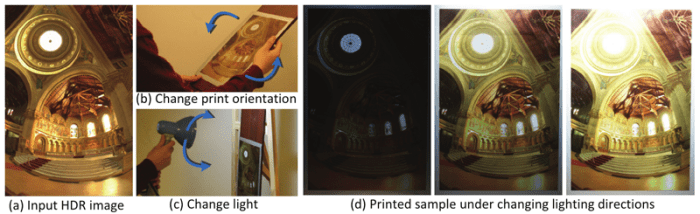
In print reproduction, shading is essential for creating depth, texture, and contrast. Several techniques are used to achieve this, including:
- Halftoning:Uses small dots of varying sizes to simulate shades of gray.
- Stochastic screening:Uses randomly distributed dots of varying sizes and shapes to create a more natural appearance.
- FM screening:Uses a fine grid of dots to produce high-quality images with minimal moiré patterns.
Factors Affecting Shading Quality, Process for reproducing shading in print
The quality of shading reproduction depends on several factors:
- Screen ruling:The number of dots per inch (dpi) determines the fineness of the shading.
- Dot shape:Round or elliptical dots produce smoother transitions, while square or diamond-shaped dots create a more defined texture.
- Ink density:The amount of ink used affects the darkness and contrast of the shading.
Process for Reproducing Shading in Print
The process of reproducing shading in print involves several steps:
- Image preparation:The image is converted to a grayscale or CMYK format and adjusted for screen ruling and dot shape.
- Platemaking:A printing plate is created with the shading information.
- Printing:Ink is transferred from the plate to paper or other substrates.
Challenges in Reproducing Shading in Print

Common challenges include:
- Moiré patterns:Interference patterns that can occur when using halftoning or stochastic screening.
- Banding:Visible lines or streaks in the shading.
- Color shifts:Variations in color between different areas of the shading.
Strategies for overcoming these challenges include using high-quality screens, optimizing ink density, and employing advanced screening techniques.
Applications of Shading in Print

Shading is widely used in print applications to:
- Create depth:Simulate three-dimensional effects by adding shadows and highlights.
- Add texture:Enhance the tactile or visual qualities of printed materials.
- Increase contrast:Emphasize important elements and improve readability.
Shading plays a crucial role in enhancing the visual appeal and effectiveness of printed products, from magazines and books to packaging and posters.
Popular Questions
What are the key factors that affect the quality of shading reproduction in print?
Screen ruling, dot shape, and ink density are the primary factors that influence the quality of shading reproduction.
What are the common challenges encountered in reproducing shading in print?
Moiré patterns, banding, and color shifts are some of the most prevalent challenges faced when reproducing shading in print.
How can I overcome the challenges of reproducing shading in print?
Understanding the causes of these challenges and implementing appropriate strategies, such as adjusting screen ruling or using specific screening techniques, can help mitigate these issues.