Back to back bends conduit, a remarkable solution for intricate electrical installations, invites us on an exploratory journey through its applications, design considerations, and safe handling practices. Get ready to unravel the secrets of this versatile conduit and discover its potential to streamline your electrical projects.
From industrial settings to residential buildings, back to back bends conduits have proven their mettle. They offer unparalleled flexibility, allowing for seamless navigation around obstacles and efficient routing of cables. Their robust construction ensures durability and longevity, making them an ideal choice for demanding environments.
Conduit Overview
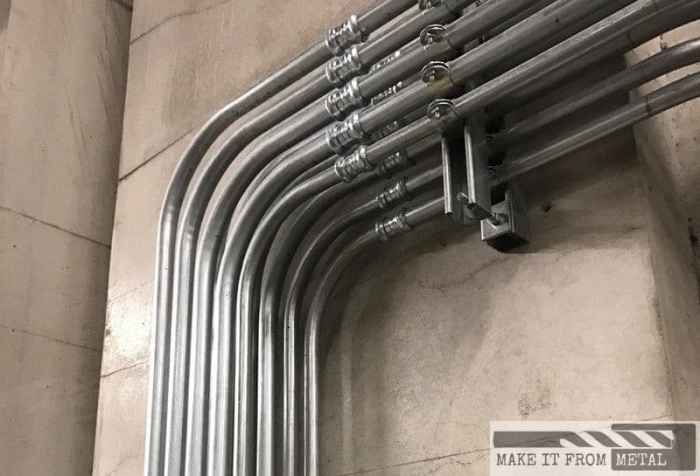

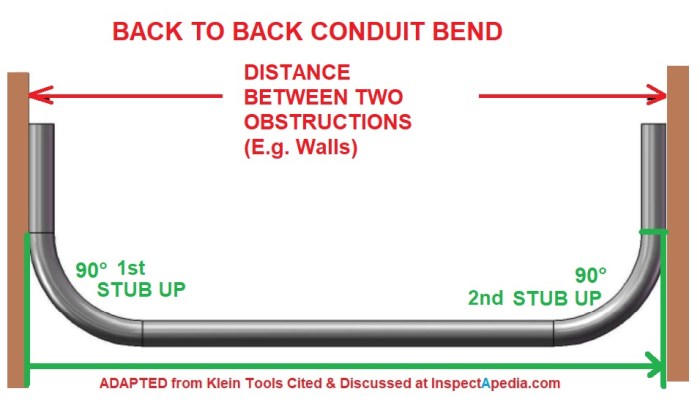
A back-to-back bends conduit is a specialized electrical conduit designed to accommodate 90-degree bends in electrical wiring systems, providing a smooth and protected transition for cables and wires.
These conduits are typically constructed from durable materials such as galvanized steel, aluminum, or PVC (polyvinyl chloride), ensuring resistance to corrosion, impact, and environmental factors.
Materials Used
- Galvanized Steel:Offers excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
- Aluminum:Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and non-magnetic, making it ideal for use in areas where weight and magnetic interference are concerns.
- PVC:Non-conductive, flexible, and easy to install, making it a popular choice for indoor wiring systems and underground applications.
Applications

Back-to-back bends conduits are extensively used in various electrical and construction applications. They offer several advantages, particularly in scenarios where space constraints or specific routing requirements exist.
One common application of back-to-back bends conduits is in industrial settings. They are ideal for routing cables and wires in tight spaces, such as control panels, machinery enclosures, and electrical cabinets. The compact design allows for efficient cable management, maximizing space utilization while maintaining a neat and organized appearance.
Electrical Distribution
In electrical distribution systems, back-to-back bends conduits play a crucial role in connecting electrical components, such as transformers, switchboards, and distribution panels. They provide a secure and reliable pathway for electrical cables, ensuring proper power distribution throughout the facility.
Commercial Buildings
Within commercial buildings, back-to-back bends conduits are commonly employed in lighting systems, power distribution, and communication networks. Their ability to navigate tight spaces and corners makes them suitable for routing cables through walls, ceilings, and under raised floors, enabling efficient and unobtrusive cable management.
Residential Construction
In residential construction, back-to-back bends conduits are frequently used in electrical wiring. They are particularly advantageous in areas with limited space, such as behind walls, above ceilings, and in crawl spaces. The compact design allows for easy installation, even in confined areas, ensuring proper cable routing and protection.
Design Considerations
Designing a back-to-back bends conduit involves several crucial factors that influence its performance and effectiveness. These factors include the conduit diameter, bend radius, and material thickness.
The conduit diameter directly impacts the flow capacity of the conduit. A larger diameter allows for a higher flow rate, while a smaller diameter restricts the flow. Selecting the appropriate diameter is essential to ensure the conduit can handle the required flow rate without causing excessive pressure drop or flow restrictions.
Bend Radius
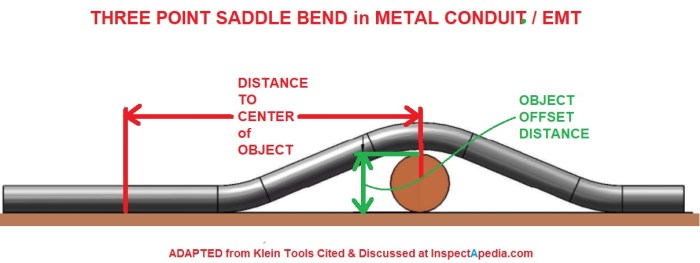
The bend radius refers to the curvature of the conduit bends. A smaller bend radius results in tighter bends, which can increase pressure drop and reduce flow efficiency. Conversely, a larger bend radius provides more gradual bends, minimizing pressure drop and maintaining flow efficiency.
The bend radius should be carefully considered to balance the need for space constraints with the desired flow performance.
Material Thickness, Back to back bends conduit
The material thickness of the conduit affects its strength and durability. A thicker conduit is more robust and can withstand higher pressures, but it also increases the weight and cost. A thinner conduit is lighter and less expensive, but it may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
The material thickness should be selected based on the specific operating conditions and performance requirements.
Installation Techniques
Installing back-to-back bends conduits requires careful planning and precise execution to ensure proper alignment and functionality. The process involves bending the conduit to the desired angles and connecting them using appropriate fittings.
Bending the Conduit
To bend the conduit, follow these steps:
- Mark the conduit at the desired bend location.
- Use a conduit bender to bend the conduit to the required angle.
- Ensure the bend is smooth and free of kinks or sharp edges.
- Repeat the process for the second bend.
Connecting the Conduit
Once the conduits are bent, they can be connected using appropriate fittings:
- Apply a layer of anti-seize compound to the threads of the fittings.
- Screw the fittings onto the conduits, ensuring they are hand-tight.
- Use a wrench to tighten the fittings further, but avoid overtightening.
- Check the alignment of the conduits and adjust as necessary.
Maintenance and Inspection: Back To Back Bends Conduit
Maintaining and inspecting back-to-back bends conduits is crucial to ensure their proper functioning and longevity. Regular checks can detect potential issues early on, preventing costly repairs or accidents.
Back to back bends conduit is a crucial component for efficient electrical installations. It’s like the Daryl Dixon of electrical wiring, providing the strength and flexibility to navigate challenging corners. Speaking of Daryl, if you’re a fan of the crossbow-wielding badass, you’ll love this daryl dixon x reader wife fanfiction.
Back to back bends conduit ensures your electrical system bends with the flow, just like Daryl’s survival instincts in the face of danger.
During inspections, look for signs of damage or wear, such as:
Signs of Damage
- Cracks or breaks in the conduit
- Dents or bends that restrict wire passage
- Corrosion or rust
- Loose or missing fittings
- Overheating or discoloration
Safety Considerations
Back-to-back bends conduits present potential hazards during handling and installation. Understanding these risks and adhering to safety guidelines is crucial for preventing accidents.
Potential Hazards
*
-*Electrical shocks
Conduits may come into contact with live electrical wires, posing a risk of electrocution.
-
-*Crushing or pinching
Conduits can crush or pinch fingers or hands during handling and bending.
-*Cuts and lacerations
Sharp edges on conduits can cause cuts or lacerations if handled improperly.
-*Tripping hazards
Loose or improperly installed conduits can create tripping hazards.
Safety Guidelines
*
-*Wear appropriate protective gear
Use gloves, safety glasses, and non-slip footwear to minimize risks.
-
-*Inspect conduits before use
Check for damage or defects that could compromise safety.
-*Use proper bending tools
Utilize conduit benders specifically designed for the task to ensure safe and accurate bending.
-*Secure conduits properly
Secure conduits firmly to walls or ceilings to prevent tripping hazards.
-*Avoid overbending
Overbending conduits can weaken them and increase the risk of breakage.
-*Handle conduits with care
Exercise caution when handling conduits to avoid crushing or pinching injuries.
-*Be aware of electrical hazards
Identify live electrical wires and take necessary precautions to avoid contact.
-*Follow manufacturer’s instructions
Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for proper handling and installation techniques.
By adhering to these safety considerations, you can minimize the risks associated with back-to-back bends conduits and ensure a safe work environment.
FAQs
What are the advantages of using back to back bends conduits?
Back to back bends conduits offer several advantages, including increased flexibility for routing cables around obstacles, reduced risk of cable damage due to sharp bends, and improved aesthetics by concealing cables within the conduit.
How do I choose the right size of back to back bends conduit?
The appropriate size of back to back bends conduit depends on the number and diameter of cables to be routed through it. Consider the current-carrying capacity of the cables and the space available for the conduit installation.
What are the safety precautions to consider when working with back to back bends conduits?
Always wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves and safety glasses. Ensure that the conduit is properly grounded to prevent electrical shocks. Avoid bending the conduit too sharply, as this can damage the cables within.